Bi-monthly news update from IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme (March 2024)
Apr 24, 2024 / IT Scholarship ProgrammeEmpower

Welcome to the March 2024 issue of Empower, the periodic newsletter of the IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme. This edition includes the following topics of note:
-
An Introduction to Vector Graphics
-
Faiz's Journey: Embracing Growth and Adaptability
An Introduction to Vector Graphics
(Collected from the site techtarhet.com)
Vector graphics are computer images created using a sequence of commands or mathematical statements that place lines and shapes in a two-dimensional or three-dimensional space.
In vector graphics, a graphic artist's work, or file, is created and saved as a sequence of vector statements. A vector graphic file describes a series of points to be connected.
These files are sometimes called geometric files. Images created with tools like Adobe Illustrator and Corel's CorelDRAW are usually vector image files.
Simplified, vector graphics are like connect-the-dots drawings.
What are vector graphics used for?
Graphic artists, illustrators and designers use vector graphics for a variety of reasons, including the following:
- Scalability. Vector formats are good for projects that require scalable graphics, including scalable type and text. For example, company and brand logos are displayed in different sizes; they show up in the corner of a mobile application or on a roadside billboard. A logo created with vector graphics can be scaled up or down without loss of quality or creating a large file.
It was the scalability feature of vector graphics that resulted in its return, after falling out of favour to raster graphics in the 1980s. Vector graphics were originally used in computer displays in the 1960s and 1970s. World Wide Web Consortium worked on Vector Markup Language, which evolved into the Scalable Vector Graphics open source language that contains vector and raster elements. - App and web development. Vector graphics are useful in application and web development because web apps and the graphics they contain must work with various screen sizes and device types. For instance, Amazon WorkLink is a mobile app that enables a fully interactive representation of corporate data on an employee's mobile device.
- Animated images are also usually created as vector files, which provide for cleaner and smoother images.
- Computer-aided design (CAD). CAD programs frequently use vector files for manufacturing, engineering and design because of their scalability and ease when it comes to editing mathematical formulas.
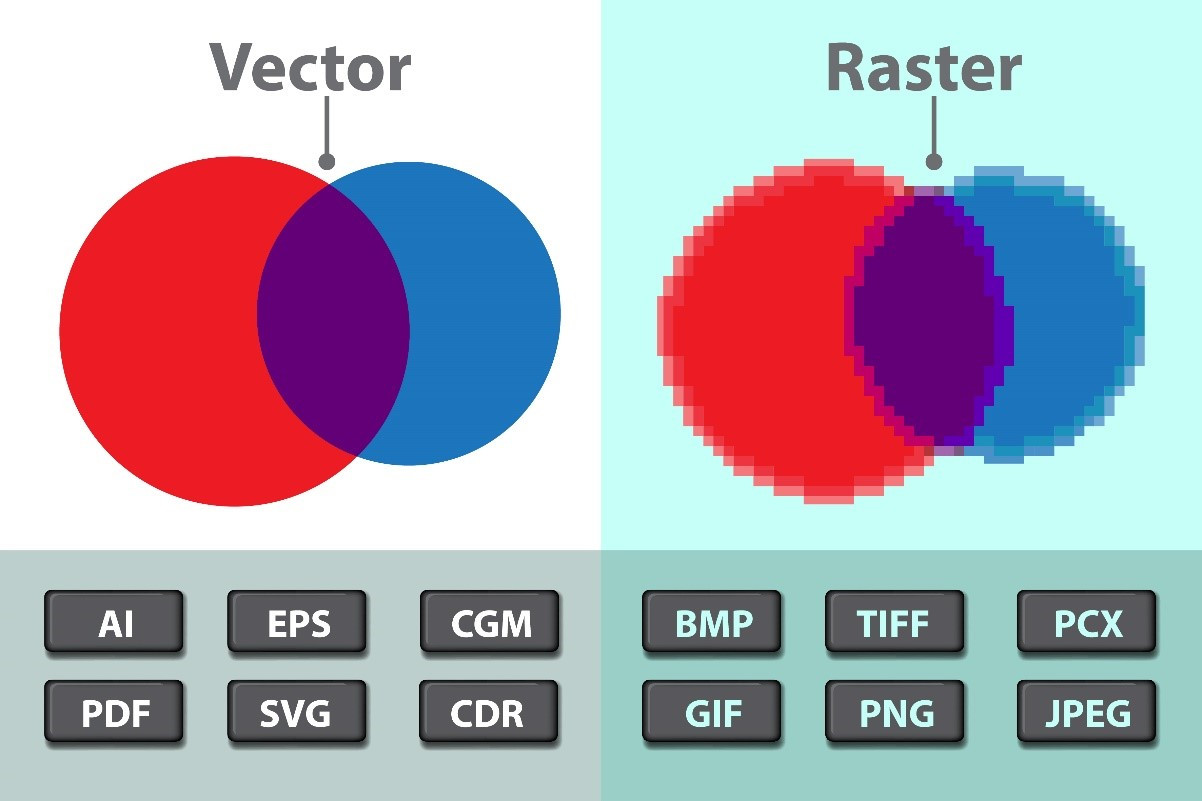
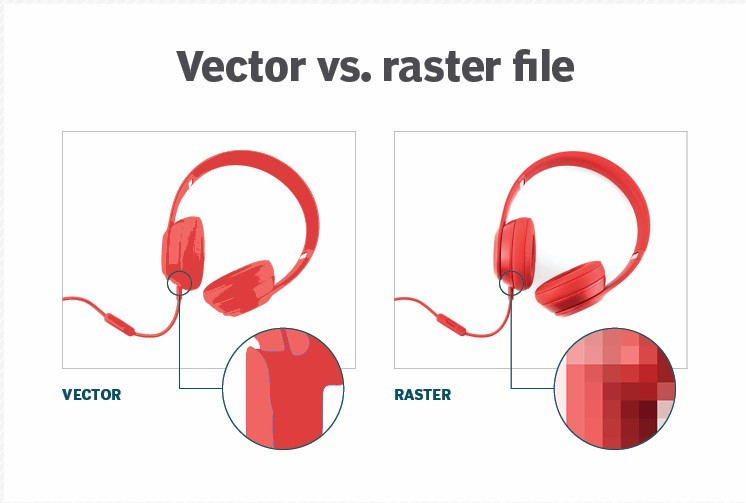
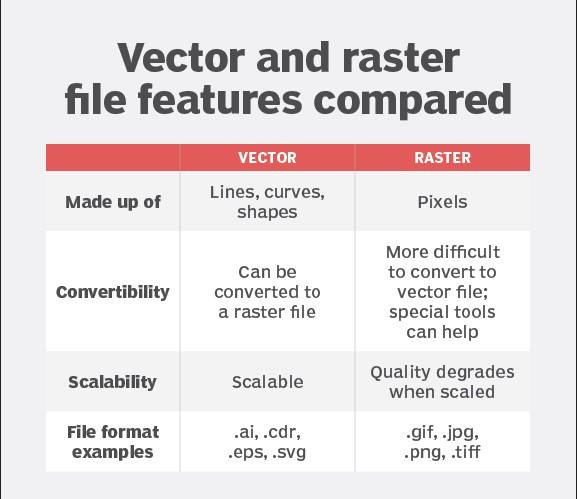
Vector vs. raster
A raster graphics image maps bits directly to a display space, also called a bitmap. Raster graphics are made up of a fixed number of pixels, which makes them less scalable than vector graphics. At a certain point, when the raster image is enlarged enough, the edges become ragged, and it appears pixelated ─ i.e., when the pixels become visible. Raster graphics cannot be scaled up without sacrificing image quality.
|
Vector and raster images can look different. This is because vector graphics must have a separate shape for each color shade, while raster images can have every pixel be a different color, showing subtle color gradations and depth more clearly. At larger sizes, the edges of raster images become ragged and the images pixilate. Vector images are more scalable |
There is also a one-to-one relationship between each pixel and the memory raster graphics occupies on a computer. Computers must store information for every pixel of a raster image, whereas vector images only store the series of points that need to be connected by lines, curves, etc. Consequently, vector files are usually smaller than raster files. Vector image files are easier to modify than raster image files for this reason.
Vector and raster images can be converted into one another with the right software. Adobe Illustrator and Adobe Photoshop are examples of software that enable users to convert one image format to the other.
Raster files are particularly good for portraying colour depth, as each pixel can be a different colour. And there are more pixels that can be unique colours than vectors that can be unique colours. This makes raster file formats good for editing digital photographs.
Certain file types can include vector and raster elements ─ PDF and SVG files are two examples.
Advantages and disadvantages of vector graphics
It is important to consider both the benefits and drawbacks of using vector files.
Advantages
- As previously mentioned, this is the main advantage of vector graphics. Because vector graphics are derived from mathematical vector relationships, or relationships between points that create lines and curves, they appear clean and exact at any size.
- Small file size. Vector graphics generally have a small file size because they only store a small number of points and the mathematical relationships between them. Those relationships are expressed in code, which is less memory-intensive compared to storing pixels.
- Easy to edit. Vector files are easy to edit because users can change vector relationships fast to swap out colours or change line shapes, for example. This is useful in an iterative process, like graphic design, that requires a lot of editing.
- Easy to load. Because file sizes are smaller, it is easy to port and load vector files to different devices and programs.
- Easy to duplicate. It is also easy to create clones of a vector image and copy certain features of one graphic to another.
- The ability to scale vector graphics up or down means they have a precise look and feel.
Disadvantages
- Less detail. Vector files are limited in dealing with complex images. For instance, photographs require colour shading and blending that vector files cannot provide as well as raster files.
- Skill and time requirements. Vector files can require more skill and time to create.
- Limited browser support. There is less support for vector graphics on web browsers than for raster graphics.
- Vector images can vary from one application to another, depending on how compatible the rendering and creating applications are, among other factors.
Types of vector files
There are several commonly used vector file types. They include the following:
- .ai ─ Adobe Illustrator File
- .cdr ─ CorelDRAW Image File
- .dxf ─ Drawing Exchange Format File
- .eps ─ Encapsulated PostScript File
- .svg ─ Scalable Vector Graphics File
- .wmf ─ Windows Metafile
Different file types are used for different tasks. For example, AI files are commonly used in print media and digital graphics. EPS files can be both raster and vector files. They typically contain a smaller design element that can be embedded in a larger design. This makes them suitable for sending logos, which are often incorporated into larger designs.
Faiz's Journey: Embracing Growth and Adaptability
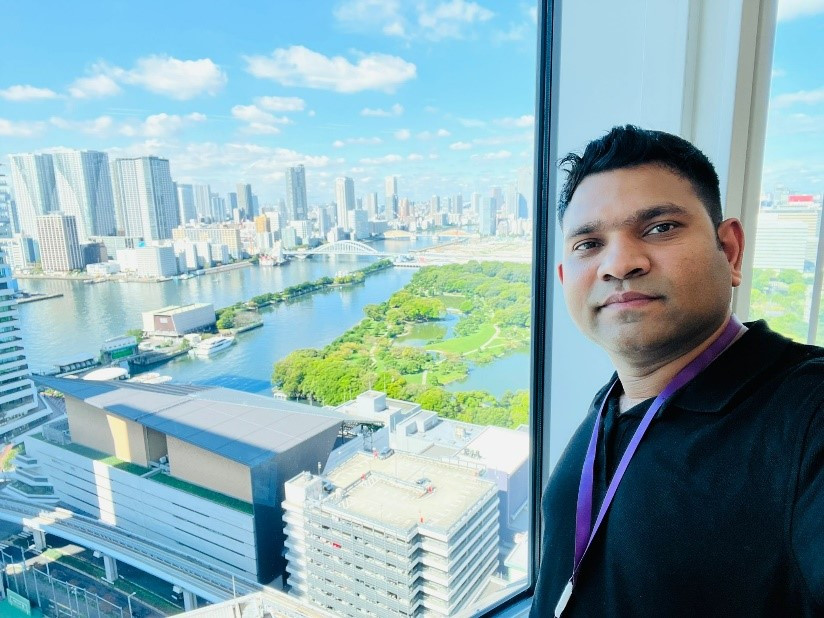

FAIZ AHMED
Round-20
Batch ID: ID-DDD/IBCS-01A/R20/01
ID: 1158424
Faiz Ahmed, an engineer at Ericsson in Yokohama, Japan, lives by the mantra "Never Stop Learning." His career path beautifully illustrates this commitment.
Initially, Faiz pursued accounting, earning top grades in his master's. He aimed for a position at a leading firm like Hoda Vasi Chowdhury & Co. However, due to a lack of connections, he faced challenges entering the field.
Rather than becoming disheartened, Faiz courageously pivoted to the rapidly evolving world of information technology. To gain the required skills, he applied for the IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme in 2013. Fully dedicated, he attended every class and extended his learning beyond formal hours. With this scholarship, Faiz earned a diploma in Database Design & Development and launched his IT career at IBCS-PRIMAX as a Junior Programmer. Over time, he grew into a skilled software engineer.
Faiz's thirst for growth led him to explore opportunities abroad. He learned basic Japanese, opening doors to job applications in Japan. In 2019, combining his IsDB-BISEW diploma and language skills, he secured a position at Zips Corporation.
Facing unexpected challenges during the Covid-19 pandemic, Faiz was laid off from Zips Corporation. Undeterred, he took on various jobs while continuously upskilling in IT. His resilience paid off when he caught the attention of Ericsson's management, who were impressed by his technical prowess and self-reliance. Today, Faiz thrives as an ICT Engineer at Ericsson, residing in Tokyo with his wife and child.
Reflecting on his journey, Faiz shares, "Every opportunity to learn and grow has been invaluable. Switching to IT after my master's, learning Japanese, and continuously enhancing my IT skills in Japan were pivotal in establishing my professional presence abroad. Above all, the IsDB-BISEW diploma was the cornerstone that transformed my career."