Bi-monthly news update from IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme (September 2025)
Nov 05, 2025 / IT Scholarship ProgrammeEmpower

Welcome to the September 2025 issue of Empower, the periodic newsletter of the IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme. This edition features the following topics of note:
-
Server-Side versus Client-Side Rendering
-
In Their Own Words – Md Anisur Rahman Soyab
Server-Side versus Client-Side Rendering
Introduction
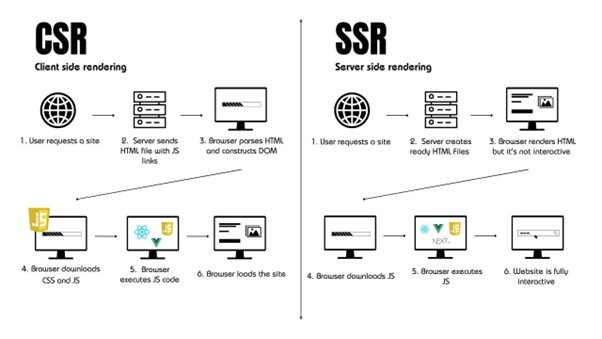
In the world of web development, server-side rendering (SSR) and client-side rendering (CSR) play a crucial role in how we experience the internet. Let’s take a journey to understand how these techniques work and why they are essential for creating engaging online experiences.
First, let’s simplify these concepts. Server-side rendering (SSR) means the server prepares web pages before showing them to you, making sure you can access the content quickly. On the other hand, client-side rendering (CSR) lets web browsers create and display content using JavaScript, making the web pages interactive and smooth.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both SSR and CSR is important. SSR is great for loading pages fast and making sure search engines can find your site. CSR is perfect for creating interactive web pages without needing to reload the whole page.
In this journey, we’ll uncover how SSR and CSR work together, impacting how websites perform and keeping users engaged. Let’s explore the essence of SSR and CSR and how they shape the ever-changing world of web development.
What is Server-Side Rendering (SSR)?
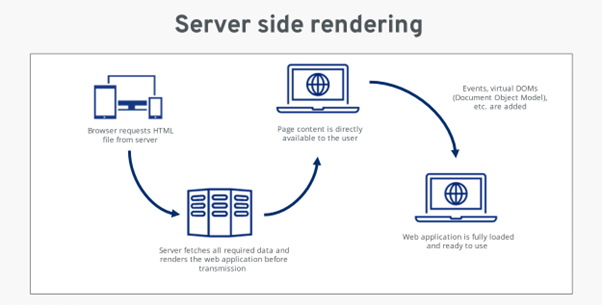
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) is a technique for rendering web pages on the server before they are sent to the client. This means that the browser does not have to download and render the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code itself. Instead, it receives a fully rendered HTML page from the server and can start displaying it immediately.
SSR offers several benefits
Faster initial page load times: SSR can significantly improve the initial page load time of a web application. This is because the browser does not have to wait for all of the resources to be downloaded before it can start displaying the page.
Better SEO: SSR is better for SEO than client-side rendering (CSR) because search engines can crawl and index the content of a page before it is sent to the client. This is because the content is already rendered in HTML when it is sent to the server.
Easier to implement: SSR is generally easier to implement than CSR, especially for complex applications. This is because the server is responsible for rendering the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code, which can be difficult to do on the client side.
SSR is used by a number of popular websites, including Google Search, Facebook, Twitter, Amazon.com, and Wikipedia.
Overall, SSR is a powerful technique that can offer a number of benefits for web applications. However, it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before deciding whether to use SSR for a particular application.
What is Client-Side Rendering (CSR)?
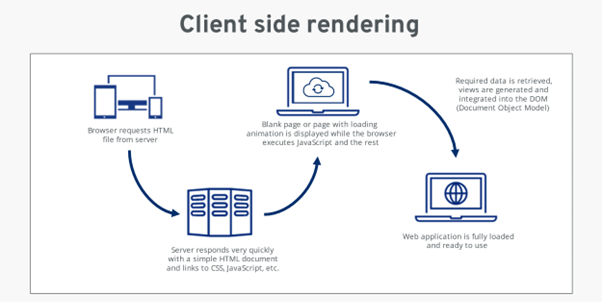
Imagine that you are going to a restaurant. With CSR, the chef would give you the ingredients and the recipe, and you would cook the meal yourself at your table. With server-side rendering (SSR), the chef would prepare the entire meal in the kitchen and then bring it to your table.
Client-side rendering (CSR) is a technique for rendering web pages on the client (browser) instead of on the server. This means that the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code is downloaded by the browser and then executed to render the page.
How does CSR work?
When a user visits a website that uses CSR, the browser sends a request to the server for the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code. The server sends back the code to the browser, and the browser then executes the code to render the page.
CSR frameworks, such as Angular and React, make it easy to develop CSR applications. These frameworks provide a number of features that make it easy to develop interactive and responsive web applications.
CSR can improve the performance of web applications by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred between the client and the server. This is because the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code is only downloaded once, and then it can be reused to render the page multiple times.
CSR can be used to create more interactive and responsive web applications. This is because the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code is executed on the client, which allows for faster updates to the page.
Examples of popular websites that use CSR:
- Google Search
- Netflix
- Gmail
Different types of CSR frameworks:
There are a number of different CSR frameworks available, including:
- Angular
- React
- Vue.js
- Ember.js
- Svelte
Every one of these frameworks possesses its unique set of advantages and drawbacks. Angular is a good choice for complex applications, while React is a good choice for simple applications. Vue.js is a good choice for beginners, while Ember.js is a good choice for experienced developers. Svelte is a good choice for applications where performance is critical.
CSR is a powerful technique that can be used to develop interactive, responsive, and secure web applications. However, it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before deciding whether to use CSR for a particular application.
CSR is generally faster than SSR, but it can be more difficult to implement. SSR is easier to implement, but it can be slower than CSR.
Which approach is better for you depends on your specific needs. If you need a fast and interactive application, then CSR is a good choice. If you need a simple and easy-to-implement application, then SSR is a good choice.
Here is a real-world example of CSR:
When you are using Google Search, the results are rendered on your browser using React. This means that the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code for the results is downloaded by your browser and then executed to render the results. This makes Google Search very fast and responsive.
Advantages and disadvantages of SSR
Advantages of SSR
Faster Initial Page Load Time: SSR significantly reduces the initial page load time as the client receives pre-rendered content from the server, resulting in a faster perceived load time.
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Benefits: Search engines can easily crawl and index content since the complete HTML is available in the initial response. This improves the discoverability and ranking of your web pages.
Better Performance on Low-End Devices: SSR is advantageous for users on low-end devices or those with slow internet connections, as most of the rendering process is handled by the server.
Disadvantages of SSR
Increased server load: SSR can increase the server load, especially for high-traffic websites. This is because the server has to render the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code for each request.
Reduced interactivity: SSR can reduce the interactivity of a web application. This is because the server has to render the entire HTML page before it can be displayed to the client. This can lead to a delay when the user interacts with the page.
When should you use Server-Side Rendering?
- When initial load times are more important than subsequent ones — storefront.
- When JavaScript and heavy interactivity is not required on the client — content website.
- When client-side routing is not required.
- When you want to offload computation and bandwidth from the client to the server.
Perfect for storefronts and content websites.
Advantages of CSR
Faster interactivity: CSR can provide faster interactivity for web applications. This is because the browser can update the page without having to make a new request to the server.
Reduced server load: CSR can reduce server load by offloading the rendering of web pages to the browser.
Greater flexibility: CSR provides greater flexibility for developing web applications. For example, CSR can be used to create dynamic and interactive applications that would be difficult or impossible to implement with server-side rendering (SSR).
Disadvantages of CSR
Slower initial page load times: CSR can lead to slower initial page load times, especially for complex applications. This is because the browser has to download and execute all of the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code before it can start rendering the page.
SEO challenges: CSR can make it more difficult for search engines to crawl and index web pages. This is because the content of the page may not be fully loaded and rendered when the search engine visits it.
When to Use CSR
- Websites with a lot of dynamic content and a focus on user experience: CSR is a good choice for websites with a lot of dynamic content, such as social media websites, e-commerce websites, and single-page applications. This is because CSR can provide faster interactivity for these types of websites.
- Websites with a high-resource audience: CSR is also a good choice for websites with a high-resource audience, such as users on desktop computers or fast internet connections. This is because CSR can reduce the server load for these websites.
- Websites with offline support: CSR can also be used to create websites that support offline functionality. For example, CSR can be used to create websites that allow users to browse content even when they are not connected to the internet.
Examples:
- Gmail
- Google Maps
- Netflix
- Spotify
The best approach for a particular application will depend on its specific needs. SSR is a good choice for websites with a lot of static content and a focus on SEO. CSR is a good choice for websites with a lot of dynamic content and a focus on user experience.
|
Aspect |
Features of Client-side rendering |
Features of Server-side rendering |
|
Execution |
User’s browser |
Web browser |
|
Languages |
Java, HTML, CSS, |
PHP, Python, Ruby, Java, ASP.Net, Node.js |
|
Primary Use |
Dynamic content updates, user interaction |
Database interaction, data processing |
|
Security |
Less code is exposed to users |
Code is hidden from the users |
|
Performance |
Server load is reduced, gives immediate feedback |
Can handle complex tasks, consistent behaviour |
|
Dependence |
Browser compatibility |
Server resources and configuration |
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of server-side rendering (SSR) and client-side rendering (CSR). We have also provided guidance on when to use SSR and when to use CSR.
SSR renders web pages on the server before they are sent to the client. This can improve the initial page load time and SEO, but it can also reduce the interactivity of the page.
CSR renders web pages on the client. This can provide faster interactivity for users, but it can also lead to slower initial page load times and SEO challenges.
The best approach for a particular web application will depend on its specific needs. SSR is a good choice for websites with a lot of static content and a focus on SEO. CSR is a good choice for websites with a lot of dynamic content and a focus on user experience.
When choosing between SSR and CSR, it is important to consider the specific needs of your web application. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
In Their Own Words – Md Anisur Rahman Soyab – From Curious Student to Senior System Administrator at Wipro
Name: Md Anisur Rahman Soyab
Senior System Administrator
Course: Networking Technologies
Round: 25


Md Anisur Rahman Soyab, a graduate of the IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme, works as a Senior System Administrator at Wipro. His fascination with computers and electronics began early in his school years, when his enthusiasm for tinkering with electronic devices was so intense that his mother once sought the principal’s help to ensure he also paid attention to his regular studies.
After completing his undergraduate degree, Soyab found himself uncertain about which career path to pursue. It was a close friend who encouraged him to apply for the IsDB-BISEW IT Scholarship Programme, knowing his long-standing passion for technology. Taking this advice to heart, Soyab applied successfully and embarked on the programme’s rigorous and highly regarded training.
He chose to specialise in networking technologies and graduated from the programme in 2016. Shortly thereafter, he began his professional journey at Desh Universal Ltd, a respected IT solutions provider. It is worth mentioning that IsDB-BISEW’s professional-level diploma earned by Soyab emboldened him to join a master’s programme in IT (PMIT) at Jahangirnagar University, which he completed in 2019.
His dedication, technical acumen, and drive for excellence eventually paved the way for him to join Wipro — a leading global information technology, consulting, and business process services company.
In his current role, Soyab is responsible for delivering robust IT infrastructure support to one of Bangladesh’s largest telecommunications companies. His career trajectory stands as a testament to the transformative power of skill development and perseverance.
Reflecting on his journey, Soyab shares:
“The IT Scholarship Programme was pivotal in opening the doors to my career in information technology. I wholeheartedly encourage graduates with a passion for IT to seize this opportunity. It’s a decision they will never regret.”



